Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antecedents and Consequences in Job Insecurity On Employee A Narrative Systematic Review
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antecedents and Consequences in Job Insecurity On Employee A Narrative Systematic Review
Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Antecedents and Consequences in Job Insecurity on
Employee:
A Narrative Systematic Review
1 2
Bella Christianty Era Ayu Amelia
Master of Psychology Master of Psychology
Gunadarma University Gunadarma University
Jakarta, Indonesia Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Siti Qori Almira
Master of Psychology
Gunadarma University
Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract:- Increased global competition due to and create uncertain working conditions (Karatepe,
continuous change results in an era of progress, especially Rezapouraghdam, & Hassannia, 2020).
in the economic sphere. The uncertain economic situation
poses a threat to employee job security. Of course, at this Of course, at this time employees feel their jobs are at
time employees feel their jobs are at stake. Job insecurity stake (Richter & Näswall, 2018). In Indonesia, the loss of jobs
is defined as a mismatch between what individuals want such as toll booth guards, since the mandatory payment with
and what individuals get. This study was conducted to electronic money has made employees lose their jobs (Badan
further discuss what are the antecedents and Pengatur Jalan Tol, 2017). In addition, some jobs are even
consequences of job insecurity in employees. This study predicted to disappear, as explained by the Minister of State-
uses a systematic review method with narrative Owned Enterprises (Badan Usaha Milik Negara/BUMN),
techniques. A total of 27 selected journals were used for Erick Thohir, that jobs such as food preparation service
review. From the analysis of this journal, the antecedents personnel, office administration personnel, transportation
of job insecurity are grouped into two, those from the service personnel, non-auto manufacturing production
organization and the environment, as well as those from personnel, construction and extraction, traditional farming,
individuals. Similarly, the consequences of job insecurity fishing, and forestry, sales and related fields, social media
are grouped into two, those to the organization and the managers, and security service personnel are expected to
individual. Thus, this study suggests organizations pay disappear by 2030, resulting in the need for competency
attention to the tendency of job insecurity in employees development of workers (CNBC Indonesia, 2022).
and handle it with open communication, employee
involvement, and job resources. Meanwhile, employees Thus, this shows that many things need to be considered
need awareness to increase personal resources. in supporting success in competition amid advancing times.
Based on research conducted by Price Waterhouse Coopers
Keywords:- Job Insecurity; Employee; Antecedents; (2022), human resources are at the first level which is a
Consequences. threatening risk to company growth so human resources are
an important means for company growth. The importance of
I. INTRODUCTION human resources for company growth certainly makes
companies strive to have employees who have abilities that
Change and renewal are constantly carried out by are relevant to what is needed in company growth. Human
humans to create an increasingly advanced era. The progress resources are not only the responsibility of a company but also
of this era, of course, has an impact on human life, including the responsibility of the employees themselves. Given, the
the economic sphere, both positively and negatively. competition that is becoming increasingly severe as a result of
Unlimited space and time is a positive impact of the times, so the times, requires employees to continue to improve their
it makes all individuals or companies the right to compete quality to be able to survive in the work competition.
freely in the international market. Where this indicates that Competition to maintain and develop careers among
there is increasing global competition (Bohle, Chambel, employees is part of job insecurity. Job insecurity is a feeling
Medina, & Cunha, 2018). Various unexpected economic of employee helplessness in maintaining the desired
situations, such as the implementation of mergers, continuity in a threatening work situation (Greenhalgh &
downsizing, outsourcing, acquisitions, the use of robots, Rosenblatt, 1984).
automation and artificial intelligence in certain jobs, and other
types of structural changes can threaten employee job security
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 955
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Job insecurity also according to Greenhalgh and at risk and employees are unable or unwilling to fight back, so
Rosenblatt (2010) influences dysfunctional work attitudes, making employees vulnerable to threatening situations.
such as decreased effort, turnover intention, and resistance to
change. Shoss (2017) also revealed that job insecurity is not Job insecurity itself is influenced by several factors,
just worried about losing a job, but job insecurity is where according to De Witte, Elst, and Cuyper (2015), three
perceptual, future oriented and uncertain, referring to the things can reduce job insecurity, which are communication,
opportunity to lose the job as a whole, deterioration in participation, and employability. Ashford, Lee, and Bobko
working conditions, and loss of anticipated opportunities. Of (1989) also gave their opinion regarding the factors of job
course, this will later affect organizational effectiveness, such insecurity, which are perceived lack of predictability and
as low productivity, high employee turnover, and low control, organizational changes, role ambiguity, and external
adaptability (Greenhalgh & Rosenblatt, 2010). In addition, job locus of control. Kinnunen (2014) added several things that
insecurity does not only cause adverse influences related to become individual factors in experiencing job insecurity
attitudes in work settings but more than that. Job insecurity related to the personal background; how the individual's
can reduce psychological well being, as well as increase position in the job, usually related to the position identified by
psychosomatic tendencies and physical strain (De Witte, the length of work and work contracts concerning working
1999). This is in line with what De Witte, Elst, and De Cuyper hours; besides that the status in the family is also a factor,
(2015) revealed that uncertainty about one's job is an where the head of the family who has a higher role in being
experience that tends to last a long time, and is harmful to responsible for supporting the family if they lose their job it
health and well being in the short and long term. The can be a big threat so that they are more vulnerable to
continuous experience of uncertainty has a cumulative impact. experiencing job insecurity; as well as attitudes and
personality.
Therefore, this study was conducted to systematically
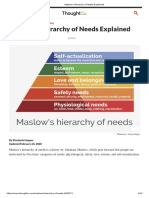
analyze the antecedents and consequences of job insecurity in Job insecurity itself has a negative impact on employees'
employees. In this study, it is hoped that both companies and physical health, mental health, and psychological well being,
employees can find out what can be the antecedents and such as increased stress, burnout, job exhaustion, and mental
consequences of job insecurity. Thus, companies can produce distress. In addition, job insecurity also has an impact on
human resources that will support the growth of the company, employee work attitudes, such as decreased job satisfaction,
and employees can improve their quality to be able to increased turnover intention, decreased trust in the
compete in their work healthily. organization, and decreased commitment to the organization
(De Witte, Elst, & Cuyper, 2015; Kinnunen, 2014; and
II. LITERATURE REVIEW Ashford, Lee, & Bobko, 1989).
According to De Witte, Elst, and De Cuyper (2015), job III. METHOD
insecurity is a mismatch between what an individual wants
(certainty about the future of the individual's current job) and A. Procedures
what the individual gets (perception of threats to the current Study to find antecedents and consequences of job
job). Job insecurity is multidimensional, as explained by insecurity in employees was conducted by reviewing literature
Hellgren, Sverke, and Isaksson (1999) that job insecurity collected from various sources, including Google Scholar,
consists of quantitative job insecurity and qualitative job Emerald, Elsevier, Routledge: Taylor and Francis Groups,
insecurity. Quantitative job insecurity is explained as Wiley Online Library, MDPI, Sciendo, SAGE Publication,
employees' worries about their current job in the future, while Academia, Springer, JSTOR, Medical Care, Peuradeun
qualitative job insecurity is related to feelings of threat due to Scientific Journal, Widya Cipta, and Atlantis Press. This study
deterioration in work relationships such as worsening working uses a systematic review method with narrative techniques in
conditions, reduced career opportunities, and decreased salary the data processing process. Narrative review is used to
development. identify a topic by summarizing, selecting, and focusing on
the literature as evidence related to the topic of interest
In addition, Greenhalgh and Rosenblatt (2010) also gave (Kosztyána, Csizmadiab, & Katona, 2021).
their opinion regarding the dimensions of job insecurity,
which are desired continuity, threat, job features, and B. Analyzed Data Criteria
powerlessness. Desired continuity, is employees do not From these sources, several journals that are suitable for
always want a permanent position, sometimes employees are the proposed study topic were collected, which are 27 journals
happy to quit, especially if there is an attractive severance with publication years 2013-2021. The keywords used during
package. Employees also sometimes want to quit if they don't the literature search are job insecurity in the workplace of
like the work situation or want a more interesting job. Threat employees, the impact of job insecurity in the workplace, job
is the employee's perception that there will be a possibility of insecurity factors, job insecurity antecedents, job insecurity
a situation that violates expectations of continuity. That is, this consequences, and job insecurity antecedents and
threat is subjective, although it may or may not happen, and consequences.
this creates job insecurity. Job features at risk, where
employees worry about changes that could lead to job loss. The journals found included the Journal of Hospitality
Powerlessness is when employees perceive that their jobs are Marketing & Management, Ethical Theory and Moral
Practice, Advances in Developing Human, Article
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 956
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Sustainability, Contemporary Educational Psychology, Resources Management Journal, and European Journal of
Studies in Business and Economics, Journal of Business Business and Management.
Research, The International Journal of Social Sciences,
Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health, Proceedings of the IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4th International Conference on Management, Economics,
and Business, Global Journal of Enterprise Information After collecting data and reviewing, it was found that job
System, European Journal of Management and Business insecurity is not just a worry felt by employees for fear of
Economics, Marketing Intelligence & Planning, South African losing their jobs (Shoss, 2017), but job insecurity also
Journal of Business Management, Problemy Zarądzania - involves satisfying the fundamental needs of employees (De
Management Issues, International Journal of Academic Witte, Elst, & De Cuyper, 2015). Where according to Maslow
Research in Business and Social Sciences, Journal of (1943), humans have five basic needs, which are
Informetrics, Journal of Secretarial and Management, physiological needs, security needs, love needs, self esteem
Economic and Industrial Democracy, Business Ethics needs, and self actualization needs. This shows that job
Quarterly, International Journal of Hospitality Management, insecurity has several consequences on individuals, not only
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public as employees but also as humans themselves. Job insecurity
Health, Journal of Business Management, Journal of can occur due to several antecedents. Antecedents and
Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, consequences found in several studies related to job insecurity
Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, Human will be described in detail in Table 1.
TABLE I. SELECTED FINDINGS FROM RELATED LITERATURE
Authors (Year) Significant Findings
The research found a negative relationship between job insecurity and organizational
performance which in this case explained that the higher the job insecurity, the lower the
Abolade (2018)
overall organizational performance, further calculations found that job insecurity had an
pp. 14-15
influence of 40,33% on organizational performance. The study also found that there is a
very strong positive relationship between job insecurity and employee turnover.
Asfaw and Chang (2019) Job insecurity decreases engagement by 37%. Further calculations show that supervisor
pp. 102 and 104 support can help reduce the negative consequences of job insecurity on engagement.
Job insecurity has a positive relationship with burnout. Job insecurity felt by employees
Aybas, Elmas, and Dündar
will increase burnout. Employees who are still working after going through redundancy,
(2015)
downsizing, and privatization programs, tend to experience "survivor syndrome", but
pp. 199
employees also anticipate losing their jobs. This leads to burnout.
There is a positive relationship between job insecurity and burnout. In addition, job
Bloom, Richter, Hallsten,
insecurity is also positively correlated with depressive symptoms. Employees who
Svedberg (2015)
experience job insecurity tend to report more complaints about symptoms of poor mental
pp. 54-57
health, such as burnout and depressive symptoms.
Significantly, job insecurity is a negative predictor of employee performance, where
Bohle, Chambel, Medina, and research results show that there is a negative relationship between job insecurity and job
Cunha (2018) performance. To minimize the negative influences of job insecurity, it is necessary to
pp. 399 and 401 develop good communication with employees in expressing their expectations of the
organization.
Job resources have a negative correlation with job insecurity. Employees who feel job
resources (such as selective staffing, continuous training in development, and career
Bouzari and Karatape (2018) opportunities) will tend to have low job insecurity. This means that these programs will
pp. 9-10 motivate employees to learn and improve skills and behavior, as well as opportunities for
career advancement in the organization, so this will reduce the job insecurity felt by
employees.
Job insecurity significantly negatively influences job satisfaction, meaning that job
Chalim (2018) satisfaction will increase if job insecurity decreases. In addition, job insecurity significantly
pp. 209 negatively influence organizational commitment, meaning that organizational commitment
will decrease if job insecurity increases.
Job insecurity is positively related to anxiety and negatively related to job satisfaction. It
Cheung, Wu, and Chi (2018)
was also found that psychological capital and perceived employability as personal
pp. 9
resources were negatively correlated with job insecurity.
Job insecurity, especially in the quantitative aspect of employees (related to worry about
threats and fear of losing their jobs), as well as its qualitative aspect (in the form of
Chirumbolo, Callea, and
perceptions of the potential loss of something important in their work) provides a negative
Urbini (2020)
relationship with task performance. While job insecurity with counterproductive work
pp. 244
behaviors has a positive relationship that can be seen from the contradictory or deviant
behavior of employees in the workplace.
Darvishmotevali and Ali The direct relationship that can be seen between job insecurity and job performance leads
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 957
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Authors (Year) Significant Findings
(2020) to a negative relationship. Where this indicates that if employees have high job insecurity,
pp. 6 it results in low job performance. Vice versa, if employee job insecurity is low, there is a
high increase in job performance.
Job insecurity is negatively related to self efficacy where insecurity means employees feel
Etehadi and Karatepe (2018) limited control and a feeling of helplessness against threats can hinder employee growth
pp. 13-14 and learning which has a negative influence on self efficacy, besides that job insecurity has
a positive influence on absenteeism or employee absence at work.
Workplace bullying is said to be one of the causes or antecedent factors of increased
Glambek, Matthlesen, Hetland, employee job insecurity. Both variables have a negative relationship, where exposure to
and Etnarsen (2014) workplace bullying ultimately makes employees feel afraid, uncomfortable when working,
pp. 261-262 and the loss of valuable aspects at work so that employees have thoughts of escape and
cause the intention to leave work within six months.
There is a positive influence between job insecurity on intention to quit. This shows that
high job insecurity in employees will tend to have a high intention to quit as well. Job
Ismail (2015)
insecurity contributes 52,6% to intention to quit. In addition, job insecurity also has a
pp. 269-272
positive influence on burnout, with a contribution of 15,9%. Managers must convey a clear
message that the organization feels responsible and values employees.
Job insecurity directly has a strong negative influence on employee work engagement.
While for cases that occur in employees with the intention of not attending work
(absenteeism) and not having non-green behaviors in the scope of work, together is the
result of the positive influence of job insecurity. In addition, job insecurity also illustrates a
positive relationship between intention to be late for work and intention to leave work
early. Based on the threat rigidity thesis, transactional theory of stress, social exchange
Karatepe, Rezapouraghdam,
theory, COR theory, and reformulation of attitude theory, it is said that the responses
and Hassannia (2020)
displayed by employees under uncertainty arising from the threat of job insecurity as a
pp. 8-9
stressor and limited job resources (training, supervisors, support) certainly trigger
employees' concerns about their security at work. From the things that have been
mentioned, finally, employees tend to respond poorly to their work, such as a decrease in
work engagement, high levels of unfriendly behavior, and an increase in absenteeism,
which in turn also results in nonattendance intentions in the form of intention to be late for
work and intention to leave work early.
Job insecurity has a significant and positive relationship with emotional exhaustion. High
levels of employee emotional exhaustion will reduce available resources and in turn, result
Lawrence and Kacmar (2016)
in a lack of ethical decision making. Of course, this will lead employees to engage in
pp. 69
unethical behavior. However, unethical behavior can be avoided or minimized by
increasing adaptability and embeddedness in the organization.
Job insecurity is negatively related to Organization Based Self Esteem (OBSE). The
Lin, Chen, Ashford, Lee, and
negative relationship between job insecurity and OBSE will also be stronger for employees
Qian (2018)
with more proactive personalities than less proactive employees. It also found that OBSE
pp. 173-174
was positively related to job performance and affective commitment.
Sense of coherence and work locus of control, have a role in predicting job insecurity.
Sense of coherence is stronger in causing job insecurity than work locus of control. It may
Pienaar and De Witte (2016) be due to the greater stability of sense of coherence in the personality construct. Sense of
pp. 40 coherence and work internal locus of control are negatively correlated with job insecurity.
That is, when someone has a high sense of coherence and work internal locus of control,
job insecurity in employees will be low, and vice versa.
Job insecurity has a negative relationship with life satisfaction of employees. It means that
Rafiq and Chin (2019) the higher the job insecurity, the lower the life satisfaction of employees. Job insecurity not
pp. 6-9 only causes stress from work but damages overall well being in various cultures and
industry settings.
By 29,3%, role ambiguity and perceived organizational change together can potentially
cause job insecurity. Perceived organizational change is higher than role ambiguity in
causing the impact of job insecurity. In the end, job insecurity has an adverse impact on
physical health by 11,4%, this is because employees live in constant fear which causes
Rajput and Talan (2017) lethargy and less time for exercise, so which later causes diseases such as diabetes,
pp. 7-8 hypertension, and so on. Meanwhile, job insecurity adversely affects mental health by
15,3%. Role ambiguity tends to make employees feel a lack of control over work, thus
making employees experience job insecurity.
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 958
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Authors (Year) Significant Findings
Job insecurity has a direct effect on decreasing employee trust, job satisfaction, and mental
Richter and Näswall (2018)
health with lower values. This means that employees have anxiety related to the future of
pp.99-10
their work which has a negative influence on employees.
There is a negative relationship between perceived job insecurity and work related well
being. Effective organizational communication and employee involvement (such as
Saeed, Hassan, Dastgeer, and
involvement in decision-making and compensation rewards) can reduce perceived job
Iqbal (2021)
insecurity in employees. Perceived employability as personal resources (such as skills and
pp. 12-16
expertise) can also prevent perceived job insecurity in employees. Then, job insecurity
ultimately has a positive relationship with emotional exhaustion.
Overall, the relationship between job insecurity and job performance is described as having
Selenko, Makikangas, Mauno, a negative relationship. It has been explained that at lower and moderate levels of intensity,
and Kinnunen (2013) job insecurity is negatively related to job performance. While at high levels, the effect is
pp. 536 less negative. This is also due to the influence of decreasing or increasing enthusiasm for
doing work, including a sense of optimism and supervision.
Job insecurity has a negative relationship with intrinsic motivation, in turn, job insecurity
will also be able to influence employee performance and behavioral outcomes
(organizational citizenship behavior, and change-oriented organizational citizenship
behavior). Intrinsic motivation is very important in generating work efforts because
Shin, Hur, Moon, and Lee employees will consider the motivation to work that arises due to interest and enjoyment at
(2019) work, regardless of the rewards that will be obtained later. If employees have high job
pp. 3 and 7-9 insecurity, then employee perceptions are directed towards feelings of not having meaning
at work and control over their work, so employees consider their efforts at work to be
meaningless. This certainly causes harm to the development of intrinsic employee
motivation which is considered very important in the development, encouragement, and
desire to achieve good results at work.
Soelton, Amaelia, and Prasetyo
Job insecurity significantly has a positive influence on burnout. It means that if employees
(2019)
feel high job insecurity in their jobs, it will increase burnout in employees.
pp. 172-173
Job insecurity has a positive correlation with work stress in employees. In addition, job
Soomro, Kundi, and Kamran insecurity is also positively correlated with deviant behavior (interpersonal deviance and
(2019) organizational deviance). In this study, it was found that employees who experience work
pp. 82-85 stress due to job insecurity are under threat of losing resources. Employees engage in
deviant behavior to recover from adverse effects or gain additional resources.
Job insecurity is negatively related to job satisfaction where high job insecurity will cause a
Stankeviˇciute, Staniškiene,
decrease in job satisfaction, affective organizational commitment, and work engagement.
and Ramanauskaite (2021)
Then based on this, job insecurity is negatively related to happiness at work, meaning that
pp. 11-12
it interferes with employee happiness at work.
There is a negative relationship between job insecurity with job satisfaction and
Vujičić, Jovičić, Lalić, Gagić,
organizational commitment. It means that the higher the job insecurity owned by
and Cvejanov (2015)
employees, the lower the job satisfaction and organizational commitment owned by
pp. 44
employees.
Based on the literature review conducted, it provides evaluation of the external environment. After reviewing
information related to several antecedents that lead to job journals, it was found that job insecurity antecedents from the
insecurity, and then consequences as a result of job insecurity organization and environment include organizational
in employees. From the results found, researchers further communication, job resources, role ambiguity, organizational
grouped the antecedents of job insecurity into two, which are change, employee involvement, and workplace bullying.
those from the organization and environment, as well as those
from individuals. Just like the antecedents, the consequences Communication in the organization aims to pass
of job insecurity are grouped into two, which are those for the information from the organization to all employees so that
organization and the individual. employees get relevant, important, and timely information
related to work, as well as the conditions and situations of the
A. Antecedents of Job Insecurity workplace (Jiang & Probst, 2014). Communication in an
organization that is timely and open, will tend to increase the
Organization and Environment predictive and control ability of employees regarding what
The causes of job insecurity in employees can come not will happen in the future, as well as provide experiences to
only internally, such as individual personalities, but also employees related to feelings of being valued and respected
externally, such as the environment and the organization by the organization (De Witte, Elst, & Cuyper, 2015).
where employees work. Hartley (1999) emphasized that job Employees who tend to feel they have information related to
insecurity arises due to individual interpretation and their working conditions will help create a sense of security
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 959
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
(Huang, Niu, Lee, & Ashford, 2012). This is supported by Workplace bullying refers to the phenomenon that
research conducted by Saeed, Hassan, Dastgeer, and Iqbal occurs to employees when targeted in negative actions by
(2021), which shows that effective communication in the coworkers or superiors where there is a formal or informal
organization will reduce job insecurity felt by employees. power imbalance that causes helplessness for various defenses
and resistance because it is hindered by the recognition of the
Job resources are various aspects of work that power. Workplace bullying can occur both in the short and
employees can use in achieving work goals; overcoming work long term, at least during the span of one time a week or for
demands and the impacts; and support employee growth, example for six months (Glambek, Matthlesen, Hetland, &
learning, and development (Wilkinson, 2022). Hobfoll (2001) Etnarsen, 2014). Bullying that occurs in the workplace is
stated that if employees face stressors that become obstacles at divided into two: (a) work related bullying which concerns the
work, then to deal with these stressors they can utilize job process of working, such as the loss of employee delegation,
resources. The application of job resources at the workplace an unfair attitude of superiors by deliberately not giving
can be in the form of implementing training and development promotions, manipulation of employee performance
programs, providing support from superiors and coworkers, evaluations, giving excessive workloads, sabotaging certain
selective staffing, and career opportunities (Bouzari & jobs and so on; (b) personal bullying concerns personal
Karatepe, 2018; Karatepe, Rezapouraghdam, & Hassannia, employees who are intimidated through various treatments
2020). Based on Bouzari & Karatepes (2018) research, added and words from coworkers or superiors, such as isolation,
that providing adequate job resources for employees can discrimination/exclusion, neglect, gossip, physical violence,
reduce job insecurity and encourage employee job personal jokes, and so on (Bartlett & Bartlett, 2011).
expectations. Where these expectations include personal Workplace bullying can be a factor that causes employee job
resources that allow employees to be motivated to learn and insecurity if the bullying treatment from coworkers is based
improve skills and behavior, to create opportunities for career on a certain threat related to job continuity that makes
advancement in the organization. With low job insecurity, employees unable to move or just fight back. Helplessness
employees will feel more satisfied at work which in turn and threats that may endanger employees over time can
employees can find various ways to realize expectations and increase job insecurity, so causing fear and worry at work
achieve target goals. (Glambek, Matthlesen, Hetland, & Etnarsen, 2014).
Role ambiguity refers to a lack of certainty, clarity, and Individual
predictability regarding work (McCormack & Cotter, 2013). After reviewing the selected journals, it was found that
According to research by Rajput and Talan (2017), role job insecurity antecedents can come from employees
ambiguity has the potential to cause job insecurity, because themselves. The antecedents of job insecurity that come from
role ambiguity tends to make employees feel a lack of control individuals are related to psychological capital, perceived
over work, thus making employees feel insecure about their employability, work internal locus of control, and sense of
jobs. coherence.
Organizational change refers to the process of change Psychological capital is a state related to the
in an organization or system that has been damaged to a more development of positive psychology in individuals
improved state (Rajput & Talan, 2017). However, according characterized by (a) efficacy to support success in challenging
to research also conducted by Rajput and Talan (2017), tasks; (b) optimism about current and future success; (c) hope,
organizational change has the potential to cause job insecurity which directs to always be on the road to goals in achieving
in employees. It is because organizational change is often success; and (d) resilience, which is to survive and rise when
perceived as a threat to employees (Lazarus & Folkman, faced with difficulties to achieve success (Luthans, Morgan,
1984), especially at the beginning of organizational change & Avolio, 2015). Meanwhile, perceived employability is
(Schumacher, Schreurs, Van Emmerik, & De Witte, 2015). At related to individual perceptions regarding the possibility of
the beginning of the change, employees do not have enough getting and keeping a job (Vanhercke, De Cuyper, & Peeters,
time and resources related to change information, so they tend 2014). Guilbert, Bernaud, Gouvernet, and Rossier (2016)
to assess organizational change as unfair (Rajput & Talan, revealed that employability will facilitate individual career
2017). outcomes, both current and long term.
Employee involvement is the involvement of Employees who have personal resources in jobs will
individuals in the overall organization and their work. Also tend to be less likely to lose their jobs, so this will reduce job
defined as a measure of a person's performance that influences insecurity in employees (Saeed, Hassan, Dastgeer, & Iqbal,
personal satisfaction (Wicaksono, 2007). Saeed (2021) based 2021). It is proven through research conducted by Cheng, Wu,
on the results of research conducted, revealed that employee and Chi (2018) that psychological capital and perceived
involvement is negatively correlated with job insecurity. It is employability which are personal resources have a negative
explained that the average employee who is involved in a job correlation with job insecurity. It shows that the higher the
reflects insecurity about the job. So that to feel safe at work, psychological capital owned by employees, the lower the job
employees are obliged to follow the applicable work insecurity owned by employees. Likewise with perceived
procedures and this is what makes them more involved. employability.
Employees tend to be involved in arrangements related to
decision making, information dissemination, and case solving.
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 960
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Sense of coherence, which is a global orientation that Research conducted by Abolade (2018) explains how job
shows the extent to which individuals have a sense of self insecurity influences organizational performance by 40.33%
confidence that tends to be dynamic and enduringly where (a) so higher job insecurity leads to lower overall organizational
stimuli from the external internal environment in the course of performance. So, high job insecurity among employees will
an individual's life are structured, predictable, and certainly hamper the organization's efforts to achieve its goals.
explainable; (b) individuals have the resources to meet the
demands arising from these stimuli; and (c) these demands are Organizational commitment is defined as the level at
a challenge that is considered worthy of individual investment which employees identify with the organization and all its
and involvement (Antonovsky, 1987). Sense of coherence is a goals and the desire to remain as part of the organization
personal resource that supports individuals to face challenges (Robbins & Judge, 2018). In line with this, Jex (2002)
and stressors in the work environment (Pearlin & Schooler, explains that organizational commitment is related to the
1978). Whereas according to Saeed, Hassan, Dastgeer, and extent of employee dedication and willingness to work for the
Iqbal (2021), personal resources in the work environment will organization. The research found that organizational
tend to make employees less vulnerable to job loss. Thus, in commitment will be low with high job insecurity (Chalim,
research conducted by Pienaar and De Witte (2016), sense of 2018; Vujičić, Jovičić, Lalić, Gagić, & Cvejanov, 2015) so
coherence is negatively correlated with job insecurity, which this explains how job insecurity influences organizational
means that the higher the sense of coherence, the lower the commitment. Furthermore, Robbins and Judge (2018) explain
perceived job insecurity. how important commitment is to employees, where if
employees currently feel unhappy with the jobs, committed
Work internal locus of control. According to Spector employees are likely to be willing to continue working for the
and O'Connell (1994), locus of control is a personality organization.
variable related to general individual expectations regarding
whether individuals can control reinforcement in their lives or Turnover intention is an individual's desire to leave the
not. Individuals who have an internal locus of control are current job consciously deliberately to find better job
individuals who have expectations that they can control opportunities in other companies (Tedja & Sijabat, 2021).
reinforcement, while individuals who have an external locus Turnover intention is divided into three cognitive categories.
of control are individuals who have expectations that force or First, thoughts of leaving refer to the employee's consideration
luck from outside is controlling the reinforcement. Thus, it is of leaving work. Second, search intention refers to the
concluded that work internal locus of control is employees employee's decision to look for work outside the organization.
who have the expectation that they can control reinforcement Third, employees have decided to leave the organization
at their work. Work internal locus of control has a negative someday. There are several reasons employees choose to
correlation with job insecurity, meaning that the higher the change jobs, including salary oriented job satisfaction factors,
work internal locus of control, the lower the job insecurity, reasons for self development, lack of comfort at work (job
and vice versa (Pienaar & De Witte, 2016). It may be because insecurity) and the environment, lack of facilities provided,
one of the dimensions of job insecurity is powerlessness, as a and related job autonomy (Priherdityo, 2016; Clercq, Azeem,
form of inability or unwillingness of employees to provide Haq, & Bouckenooghe, 2020). In connection with these
resistance (Greenhalgh & Rosenblatt, 2010) so that when reasons, based on the results of the study also found that there
employees feel that can control work, job insecurity felt by is a very strong positive relationship between job insecurity
employees decreases. As stated by Greenhalgh & Rosenblatt and employee turnover (Abolade, 2018).
(1984), that powerlessness tends to be disturbing for
employees who have internal locus of control. Organization based self esteem (OBSE) was defined
by Pierce, Gardner, Cummings, and Dunham (1989) as an
B. Consequences of Job Insecurity employee's belief to fulfill needs by participating in the
organization, where employees see themselves as important
Organization and can be useful as members of the organization. The
Job insecurity felt by employees can have an impact on research found that OBSE will be high if employee job
the organization in various aspects. Based on a review of the insecurity is low (Lin, Chen, Ashford, Lee, & Qian, 2018).
literature, it was found that the consequences of job insecurity OBSE is a belief that employees have in their role in the
on organizations are that it influences organization organization which will further lead to the performance
performance, organizational commitment, turnover intention, produced during work. Research conducted by Lin, Chen,
organization based self esteem, job performance, task Ashford, Lee, and Qian (2018) also found that OBSE is
performance, work related well being, happiness at work, positively related to job performance, where increasing OBSE
work stress, burnout, organizational citizenship behavior, job will also increase job performance.
satisfaction, work engagement, and counterproductive work
behaviors. Job performance is a set of activities and processes
carried out by employees in their work to achieve certain
Organization performance relates to the extent to goals. The research found that job performance will increase
which the performance of the organization moves to achieve if job insecurity in employees is low (Bohle, Chambel,
its goals. Organizational performance is the cumulative result Medina, & Cunha, 2018; Darvishmotevalia & Ali, 2020;
of the overall performance of its employees, where employee Selenko, Makikangas, Mauno, & Kinnunen, 2013). Job
performance can be affected if employees feel job insecurity. performance is the overall value of the work done by
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 961
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
employees during a certain time where the results will help Work stress is explained by the World Health
the organization achieve its goals (Motowidlo, Borman, & Organization (2020) as an individual response when faced
Schmit, 1997). Job performance consists of three dimensions, with job demands and pressures that do not match the
job dedication, interpersonal facilitation, and task employee's knowledge and ability to cope. In this case WHO
performance. Where job insecurity affects one of the explains that one of the things that can lead to stress is work
dimensions of job performance, which is task performance of context such as job status, where it relates to job insecurity.
employees (Wyland, Lester, Mone, & Winkel, 2013). Task Research by Soomro, Kundi, and Kamran (2019) also
performance is a combination of employee effectiveness and confirms that increasing job insecurity in employees will also
efficiency in performing core job tasks (Robbins & Judge, increase the work stress experienced. In addition, job
2018). Motowidlo, Borman, and Schmit (1997) explain that insecurity can also lead to burnout which in the APA
task performance has two types, where the first is related to Dictionary of Psychology (2015) is defined as physical,
the activity of converting raw materials into goods or services emotional, or mental fatigue in individuals accompanied by
as a result, and the second is related to the activities of decreased motivation, performance, and the emergence of
serving, maintaining, and distributing products, or preparing negative attitudes towards both self and others. Research has
planning, coordination, supervision to run effectively and found the influence of job insecurity on burnout, in which
efficiently. Research by Chirumbolo, Callea, & Urbini (2020) case high job insecurity leads to high employee burnout
found that high job insecurity will be associated with low task (Aybas, Elmas, & Dündar, 2015; Bloom, Richter, Hallsten, &
performance. So job insecurity will certainly harm the Svedberg, 2015; Ismail, 2015; Soelton, Amaelia, & Prasetyo,
organization in achieving goals due to the poor performance 2019). Work stress and burnout are employee conditions that
produced by employees on core work and as a whole. are feared will have an impact on their work activities so that
they can harm the organization. Therefore, stress and burnout
Work related well being can be basically understood by must be addressed as soon as possible to ensure the long term
looking at the meaning of the word well being itself. In the sustainability of the organization (Kerr, 2022).
APA Dictionary of Psychology (2022) well being is explained
as happiness and satisfaction in individuals, with low stress Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) is defined
levels, and having good physical, mental, or quality of life by Robbins and Judge (2018) as voluntary behavior
health. Scott-Jackson and Mayo (2018) explain that work performed by employees that is not part of the employee's
related well being emerges as a form of concern for employee formal job requirements, and contributes psychologically and
health both physical and mental and sees it from the builds the social environment in which he works. OCB is one
perspective of individual well being, where performance or of many aspects related to employees with organizations
business results are not too concerned. Research finds work where its application will be beneficial to the organization.
related well being will increase with low perceived job OCB is a behavior performed that can help the organization
insecurity (Saeed, Hassan, Dastgeer, & Iqbal, 2021). become more efficient and effective (Organ, Podsakoff, &
Rothmann and Cooper (2008) assert that one of the MacKenzie, 2006). Confirming this, Gemmiti (2007)
contributing factors to low well being in employees is the explained that OCB is an important aspect for the
absence of job security such as job security in the near future organization to function optimally which is closely related to
and being able to remain at the same level of work. The effect the overall productivity of the organization through the
of poor well being will affect the work performance of behavior of its employees. OCB includes employees who
employees when it has crossed the tolerable threshold so it speak positively about their organization, help other
will further affect the organization as a whole (Rothmann & employees, and do more than the expectations given for their
Cooper, 2008). work (Robbins & Judge, 2018). Based on research, employee
OCB can be influenced by job insecurity (Shin, Hur, Moon, &
Happiness at work is identified by Jones (2010) as a Lee, 2019). Therefore, knowledge and arrangements related to
mindset that allows individuals to maximize performance and job insecurity are needed so that it does not cause effects that
potential at work, by paying attention to how when working are feared to reduce the value and function of the
alone or in groups. Fisher (2010) states that one of the factors organization.
that cause employees to feel insecure at work is the lack of
happiness at work. As the saying goes that happy employees Job satisfaction is explained by Tangkilisan (2007) as
are productive employees, it turns out to be true. Happiness at the level of pleasure felt by employees for their role or work
work includes feelings of pleasure related to how the job is, in the organization. Job satisfaction can affect employee
what the characteristics of the job are, to the overall behavior which will further affect the function and
organizational context (Fisher, 2010; Stankeviˇciute, performance of the organization as a whole (Spector, 2022).
Staniškiene, & Ramanauskaite, 2021). In line with this Employees who have satisfaction at work also feel positive
statement, based on research conducted by Stankeviˇciute, feelings related to work, while employees who do not feel
Staniškiene, & Ramanauskaite (2021), the results found that satisfied will have negative feelings (Robbins & Judge, 2018).
job insecurity is negatively related to happiness at work. Job Robbins and Judge (2018) continued that job satisfaction can
insecurity is considered one of the stressors that interfere with affect job performance and organizational citizenship
and reduce employee happiness at work. behavior in employees, whereas job dissatisfaction can lead to
counterproductive work behavior such as absenteeism and
turnover. Based on this, it is important to pay attention to
employee situations that can lead to dissatisfaction, which one
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 962
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
is job insecurity. The research found that low job satisfaction Physical and mental health, the research conducted by
is a consequence of high job insecurity (Chalim, 2018; Rajput and Talan (2017) shows that job insecurity has a
Cheung, Wu, & Chi, 2018; Richter & Näswall, 2018; negative impact on physical health and mental health.
Stankeviˇciute, Staniškiene, & Ramanauskaite, 2021; Vujičić, Physical health deteriorates as a result of job insecurity,
Jovičić, Lalić, Gagić, & Cvejanov, 2015). because employees live in constant fear, causing lethargy and
lack of time for exercise, which will eventually lead to
Work engagement is defined as a mind filled with diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and so on (Rajput &
positive feelings, satisfaction with work, characterized by Talan, 2017). Employees who experience job insecurity report
passion and dedication to the job (Schaufeli, Salanova, more complaints about symptoms of poor mental health, such
Gonzales-Roma, & Bakker, 2002). Employees who are as depressive symptoms (Bloom, Richter, Hallsten, &
engaged with the work tend to feel like achieving more Svedberg, 2015). Research conducted by Cheung, Wu, and
challenging goals. It is not uncommon for employees to exert Chi (2018) also shows that job insecurity is positively
full capacity in solving problems and developing innovative correlated with anxiety. Similarly, research conducted by
services related to employees personal commitment in order Lawrence and Kacmar (2016) showed that job insecurity has a
to realize their goals (Bakker & Leiter, 2010). If employees no significant positive relationship with emotional exhaustion.
longer feel fully connected to the job role, there may be a
stressor that is hindering employee growth, development, and Self efficacy refers to an individual's feeling of belief in
learning orientation. One such stressor is job insecurity, which the ability to carry out and organize what actions are needed
can reduce the intensity of engagement of employees when to manage situations that have prospects (Bandura, 1997). Self
working. Job insecurity is said to have the potential to thwart efficacy can be influenced by the emotional arousal of
employee efforts and impede employee progress toward situational circumstances (Bandura, 1976). When situations
ultimate achievement. Employees will find their jobs no with more difficult performances with higher feared risks,
longer challenging. Where this describes the situation when cause individuals to experience fear and unbearable obstacles,
employees no longer feel safe, then employees will not fully so will not do what is feared (Bandura, 1976). It is also what
work engagement. The reason is that employees certainly feel is said in research conducted by Etehadi and Karatepe (2018)
worried about the results of their work and even experience that when employees experience insecurity, that is, with
greater frustration (Karatepe, Rezapouraghdam, & Hassannia, limited control and a feeling of helplessness against threats
2020). This statement is proven through research results that can hinder employee growth and learning which has a
high job insecurity will cause decrease in work engagement, negative impact on self efficacy.
where job insecurity directly has a strong negative influence
on employee work engagement (Karatepe, Rezapouraghdam, Intrinsic motivation is defined by Ryan and Deci
& Hassannia, 2020; Stankeviˇciute, Staniškiene, & (2000) as a form of encouragement to do an activity based on
Ramanauskaite, 2021). pleasure and inner satisfaction where the movement is not
based on rewards or accompanying pressure from outside.
Counterproductive work behaviors (CWBs) refer to Intrinsic motivation is very important for individuals because
any employee behavior that is intentionally performed and it is a self initiative in completing work. In motivated
judged to be contrary to the legitimate interests of an employees, it means that there is energy that is activated to
organization. The focus here is more on how the behavior achieve work goals. The opposite is also true in the case of
itself, regardless of what the consequences are afterward unmotivated employees. Ryan and Deci (2000) continue that
(Gruys & Sackett, 2003). Chirumbolo, Callea, and Urbini one factor that influences intrinsic motivation comes from
(2020) stated that several studies that discussed the positive situational and contextual. Where examples that often occur to
relationship between job insecurity and CWB found that employees are related to feelings of insecurity when working.
employees who often engage in deviant behaviors show a Research conducted by Shin, Hur, Moon, and Lee (2019)
tendency towards insecurity in the workplace. Related job stated that employees who have high job insecurity can direct
insecurity has been discussed in the research of Karatepe, their perceptions and feelings that they do not fully have a
Rezapouraghdam, and Hassannia (2020), revealed that the bond and meaningfulness in work. Therefore, control over
response to job insecurity in employees is a sense of worry their work decreases so employees consider their efforts at
about employees' security at work which is triggered by work to be meaningless. From this, it is known that job
uncertainty, and the end it makes employees tend to behave insecurity has a negative relationship with employee intrinsic
poorly towards their work, such as a decrease in work motivation, which can hinder attachment, fulfillment of
engagement, high levels of nongreen behavior, and an autonomy, and hinder employee efforts in achieving good
increase in absenteeism, which in turn also results in results when working due to decreased interest and enjoyment
nonattendance intentions in the form of intention to be late for at work.
work and intention to leave work early.
Trust generally refers to a strong belief in the truth,
Individual strength, ability, and reliability of an individual or
Based on the review conducted in the selected journals, organization, and this belief is a form of readiness to be
job insecurity has consequences on the individual itself, which vulnerable to the behavior of others, meaning that it is
are related to physical and mental health, self efficacy, detached from its ability to control (Wilkins, 2018). Richter
intrinsic motivation, and trust. and Näswall (2018) said that the decrease in trust based on
previous research has been a consequence of employee
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 963
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
insecurity at work. More specifically, it explains how Similarly, the consequences of job insecurity consist of
employees lose trust in an organization. On the other hand, organizations and individuals. Consequences of job insecurity
Lahno (2001) considers trust as a rational action and in the organization include organizational performance,
emotional response, and therefore if individuals have put a organizational commitment, turnover intention, organization
sense of trust in something, then individuals will be able to based self esteem, job performance, task performance, work
bear the risk of trusting decisions in certain ways. In the related well being, happiness at work, job stress, burnout,
context of employees who have high trust in the organization, organizational citizenship behavior, job satisfaction, work
it indicates that employees have an interest and a sense of engagement, and counterproductive work behaviors.
belonging to the same values. However, research conducted Summarized from the results found, job insecurity has an
by Richter and Näswall (2018), it was found that employees impact on overall organizational performance which can
have job insecurity, which has a direct effect on reducing trust hinder the organization in its efforts to achieve its goals.
to a low level. The result that often occurs is a poor Meanwhile, the consequences of job insecurity on individuals
relationship between superiors and subordinates, in addition, include physical and mental health, self efficacy, intrinsic
there comes a feeling of disappointment because of the loss of motivation, and trust. In this case, job insecurity affects
the employee's belief system in organizational integrity (how employees' physical and mental health, beliefs, interests, and
the organization treats employees fairly regarding the even the beliefs that employees have as individuals. The
fulfillment of promises of employee rights), and employees consequences of job insecurity that have been described, show
feel threatened about the future of their work which makes that job insecurity is quite important to be considered, where
employees feel insecure about their jobs. Of course, if there is to reduce job insecurity felt by employees, is not only the
no mutual trust in each other, then all parties can be affected responsibility of the organization, but also the responsibility
(negative effects on employees and downsizing of the of the employees themselves.
organization).
Researchers suggest paying attention to the antecedents
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION of job insecurity. The results of this study are expected to be
useful, especially for the human resource department and
Job insecurity threatens employees' future employment managers to better recognize the indications of employees
and the satisfaction of fundamental needs met by employees. who experience concerns regarding the future of their work, a
Job insecurity perceived by employees, of course, will questionnaire can be used to measure the level of job
ultimately affect the effectiveness and productivity of an insecurity of employees or self reported by employees. In
organization. In addition, this also indicates that job insecurity addition, organizations can implement an open
not only has an impact on employees and organizations within communication system, increase engagement, build a
the scope of work, but job insecurity can also have an impact supportive work culture, facilitate access to counseling, and
on other aspects of life as individuals themselves. Thus, this provide facilities for employees for learning and development,
study was conducted to provide an understanding of job so that in the end it can support the demands of the tasks that
insecurity, especially related to the antecedents and must be performed. Job insecurity, which is characterized by
consequences of job insecurity in employees. subjective perceptions, makes organizations need to pay
attention to job resources and employees pay attention to
This study used 27 selected journals based on personal resources as mentioned earlier to be able to make
predetermined criteria in accordance with the research employees feel they have control and the ability to predict the
objectives to be reviewed. After reviewing, the antecedents future so that employees tend to feel less job insecurity. One
and consequences of job insecurity were grouped into two. way that employees can support current and future needs is by
Antecedents of job insecurity are grouped into which come honing their skills and learning new skills through learning
from the organization and the environment, as well as those media available offline and online. Future research can use
from individuals. In the organization and environment, it different techniques that are more supportive of widespread
consists of communication in the organization, job resources, data exploration, such as cross sectional approaches,
role ambiguity, organizational change, employee involvement, longitudinal data collection, and self reported. In depth
and workplace bullying. Meanwhile, in individuals, there are analysis can also be conducted to pay attention to differences
psychological capital, perceived employability, sense of through demographic data, making the research more
coherence, and work internal locus of control. Antecedents meaningful with various supporting literature evidence.
that come from individuals show that job insecurity is not
only the responsibility of the organization but also the REFERENCES
responsibility of the employees themselves. The definition
given by De Witte, Elst, and De Cuyper (2015) also reveals [1]. Abolade, D. A. (2018). Impact of employees’ job
the subjective perceptions of the employees themselves, so insecurity and employee turnover on organisational
that one employee may feel insecure about his job, but performance in private and public sector organisations.
another employee feels confident enough to maintain his job. Studies in Business and Economics, 13(2), 5-19. doi:
So, antecedents that come from individuals also need to be 10.2478/sbe-2018-0016
considered.
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 964
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
[2]. American Psychological Association. (2022). Well- [17]. Chirumbolo, A., Callea, A., & Urbini, F. (2020). Job
being. https://dictionary.apa.org/well-being insecurity and performance in public and private
[3]. Antonovsky, A. (1987). Unraveling the mystery of sectors: A moderated mediation model. Journal of
health: How people manage stress and stay well. San Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance,
Fransisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers. 7(2), 237-253. doi: 10.1108/JOEPP-02-2020-0021
[4]. Asfaw, A. G., & Chang, C. C. (2019). The association [18]. Clercq, Azeem, Haq, & Bouckenooghe, D. (2020). The
between job insecurity and engagement of employees at stress-reducing effect of coworker support on turnover
work. Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health, 34(2), intention: Moderation by political ineptness and
96-110. doi: 10.1080/15555240.2019.1600409 despotic leadership. Journal of Business Research, 111,
[5]. Ashford, S. J., Lee, C., & Bobko, P. (1989). Content, 12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.01.064
causes, and consequences of job insecurity: A theory- [19]. CNBC Indonesia. (2022). 9 Jenis pekerjaan yang akan
based measure and substantive test. Academy of hilang di 2030, anda termasuk?.
Management Journal, 32(4), 803-829 https://www.cnbcindonesia.com/news/20220623080715
[6]. Aybas, M., Elmas, S., & Dündar, G. (2015). Job -4-349521/9-jenis-pekerjaan-yang-akan-hilang-di-2030-
insecurity and burnout: The moderating role of anda-termasuk
employability. European Journal of Business and [20]. Darvishmotevali, M., & Ali, F. (2020). Job insecurity,
Management, 7(9), 195-202. subjective well-being and job performance: The
[7]. Badan Pengatur Jalan Tol. (2017). Mulai hari ini 31 moderating role of psychological capital. International
oktober pengguna tol wajib pakai uang elektronik. Journal of Hospitality Management, 87, 1-10. doi:
https://bpjt.pu.go.id/berita/mulai-hari-ini-31-oktober- 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102462
pengguna-tol-wajib-pakai-uang-elektronik [21]. Darvishmotevali, M., & Ali, F. (2020). Job insecurity,
[8]. Bakker, A., & Leiter, M. P. (2010). Work engagement: subjective well-being and job performance: The
A handbook of essential theory and research. Britania moderating role of psychological capital. International
Raya: Taylor & Francis. Journal of Hospitality Management, 87, 1-10. doi:
[9]. Bandura, A. (1976). Social learning theory. New 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102462
Jersey: Prentice Hall. [22]. De Witte, H. (1999). Job insecurity and psychological
[10]. __________ (1997). Exercise of personal and collective well-being: review of the literature and exploration of
efficacy in changing socities. In A. Bandura (Eds.), Self- some unresolved issues. European Journal of Work and
efficacy in changing socities (pp. 1-45). Cambridge Organizational Psychology, 8(2), 155-177. doi:
University Press. 10.1080/135943299398302
[11]. Bartlett, J. E., & Bartlett, M. E. (2011). Workplace [23]. De Witte, J., Elst, T. V., De Cuyper, N. (2015). Job
bullying: An integrative literature review. Advances in insecurity, health and well-being. In J. Vouri, R. Nlonk,
Developing Human Resources, 13(1), 69-84. doi: & R. H. Price (Eds.), Sustainable working lives:
10.1177/1523422311410651 Managing work transitions and health throughout the
[12]. Blom, V., Richter, A., Hallsten, L., & Svedberg, P. life course (pp. 109-128). Springer Science + Business
(2015). The associations between job insecurity, Media. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9798-6_7
depressive symptoms and burnout: The role of [24]. Etehadi, B., & Karatepe, O. M. (2018): The impact of
performance-based self-esteem. Economic and job insecurity on critical hotel employee outcomes: The
Industrial Democracy, 39(1), 48-63. doi: mediating role of self-efficacy. Journal of Hospitality
10.1177/0143831X15609118 Marketing & Management, 28(6), 665-689. doi:
[13]. Bohle, S. A. L., Chambel, M. J., Medina, F. M., & 10.1080/19368623.2019.1556768
Cunha, B. S. D. (2018). The role of perceived [25]. Fisher, C. D. (2010). Happiness at work. International
organizational support in job insecurity and Journal of Management Reviews, 12(4), 384–412. doi:
performance. Journal of Business Management, 58(4), 10.1111/j.1468-2370.2009.00270.x
393-404. doi: 10.1590/S0034-759020180405 [26]. Gemmiti, M (2007). The relationship between
[14]. Bouzari, M., & Karatape, O. M. (2018). Antecedents organizational commitment, organizational
and outcomes of job insecurity among salespeople. identification and organizational citizenship behavior.
Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 36(2), 290-302. Seminar Paper. Munich: Grin.
doi: 10.1108/MIP-11-2017-0314 [27]. Glambek, M., Matthlesen, S. B., Hetland, J., &
[15]. Chalim, A. S. (2018). Effect of job-insecurity, Etnarsen, S. (2014). Workplace bullying as an
organizational commitment, job satisfaction on turnover antecedent to job insecurity and intention to leave: A 6-
intention: A case study of newcomer lecturers at private month prospective study. Human Resource
islamic universities in east java province, indonesia. Management Journal, 24(3), 255-268. doi:
Jurnal Ilmiah Peuradeun, 6(2), 199-214. doi: 10.1111/1748-8583.12035
10.26811/peuradeun.v6i2.284s [28]. Greenhalgh, L., & Rosenblatt, Z. (1984). Job insecurity:
[16]. Cheung, F. Y. L., Wu, A. M. S., & Chi. L. C. (2018): Toward conceptual clarity. Academy of Management
Effect of job insecurity, anxiety and personal resources Review, 9(3), 438-448.
on job satisfaction among casino employees in macau: [29]. _____________________________. (2010). Evolution
A moderated mediation analysis, Journal of Hospitality of research on job insecurity. International Studies of
Marketing & Management, 28(3), 379-396. doi: Management & Organization, 40(1), 6-19. doi:
10.1080/19368623.2019.1525332 10.2753/IMO0020-8825400101
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 965
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
[30]. Gruys, M. L. & Sackett, P. R. (2003). Investigating the [44]. Lanho, B. (2001). On the emotional character of trust.
dimensionality of counterproductive work behavior. JSTOR: Ethical Theory and Moral Practice, 4(2), 171-
International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 189. doi: 10.1023/A:1011425102875
11(1), 30-42. doi: 10.1111/1468-2389.00224 [45]. Lawrence, E. R., & Kacmar, K. M. (2016). Exploring
[31]. Guilbert, L., Bernaud, J. L., Gouvernet, B., & Rossier, the impact of job insecurity on employees’ unethical
J. (2016). Employability: Review and research prospect. behavior. Business Ethics Quarterly, 27(1), 39-70. doi:
International Journal Education Vocational Guidance, 10.1017/beq.2016.58
16(1), 69-89. doi: 10.1007/s10775-015-9288-4 [46]. Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal
[32]. Hartley, J. (1999). Models of job insecurity and coping and coping. New York: Springer.
strategies of organization. In Ferrie, J. E., Marmot, M. [47]. Lin, X. S., Chen, Z. X., Ashford, S. J., Lee, C., & Qian,
G., Griffiths, J., & Ziglio, E. (Eds.). Labour market J. (2018). A self-consistency motivation analysis of
changes and job insecurity: A challenge for social employee reactions to job insecurity: The roles of
welfare and health promotion, (pp. 127-150). organization-based self-esteem and proactive
Copenhagen: WHO regional publication. personality. Journal of Business Research, 92, 168-178.
[33]. Hellgren, J., Sverke, M., & Isaksson, K. (1999). A two- doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.07.028
dimensional approach to job insecurity: Consequences [48]. Luthans, F., Morgan, C. M. Y., & Avolio, B. J. (2015).
for employee attitudes and well-being. European Psychological capital and beyond. New York: Oxford
Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 8(2), University Press.
179-195. [49]. Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation.
[34]. Hobfoll, S. E. (2001). The influence of culture, Psychological Review, 50(4), 370-396. doi:
community, and the nested-self in the stress process: 10.1037/h0054346
Advancing conservation of resources theory. Applied [50]. McCormack, N., & Cotter, C. (2013). Managing
Psychology: An International Review, 50(3), 337-421. burnout in the workplace. Oxford: Chandos Publishing.
doi: 10.1111/1464-0597.00062 [51]. Motowidlo, S. J., Borman, W. C., & Schmit, M. J.
[35]. Huang, G. H., Niu, X., Lee, C., & Ashford, S. J. (2012). (1997). A theory of individual differences in task and
Differentiating cognitive and affective job insecurity: contextual performance. Human Performance, 10(2),
Antecedents and outcomes. Journal of Organizational 71-83. doi: 10.1207/s15327043hup1002_1
Behavior, 33(6), 752-769. doi: 10.1002/job.1815 [52]. Organ, D. W., Podsakoff, P. M., & MacKenzie, S. B.
[36]. Ismail, H. (2015). Job insecurity, burnout and intention (2006). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature,
to quit. International Journal of Academic Research in antecedents, and consequences. Thousand Oaks: Sage
Business and Social Sciences, 5(4), 263-277. doi: Publications.
10.6007/IJARBSS/v5-i4/1573 [53]. Pienaar, J., & De Witte, H. (2016). Work locus of
[37]. Jex, S. M. (2002). Organizational psychology: A control and sense of coherence as antecedents of job
Scientist-practitioner approach. Hoboken: John Wiley insecurity. South African Journal of Business
& Sons. Management, 47(3), 35-43. doi:
[38]. Jiang, L., & Probst, T. M. (2014). Organizational 10.4102/sajbm.v47i3.66
communication: A buffer in times of job insecurity? [54]. Pierce, J. L., Gardner, D. G., Cummings, L. L., &
Economic and Industrial Democracy, 35(3), 557-579. Dunham, R. B. (1989). Organizational-based self-
doi: 10.1177/0143831X13489356 esteem: Construct definition, measurement, and
[39]. Jones, J. P. (2010). Happiness at work: Maximizing validation. Academy of Management Journal, 32(3),
your psychological capital for success. Oxford: John 622-648. doi: 10.2307/256437
Wiley & Sons Ltd. [55]. Price Waterhouse Coopers. (2022). Pwc’s global
[40]. Karatepe, O. M., Rezapouraghdam, H., & Hassannia, R. workforce hopes and fears survey 2022.
(2020). Job insecurity, work engagement and their https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/workforce/hopes-
effects on hotel employees’ nongreen and and-fears-2022.html
nonattendance behaviors. International Journal of [56]. Priherdityo, E. (2016). Milenial, generasi kutu loncat
Hospitality Management, 87, 1-12. doi: pengubah gaya kerja. CNN Indonesia.
10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102472 https://www.cnnindonesia.com/gaya-
[41]. Kerr, D. (2022). Key elements of stress, exhaustion, and hidup20161215174236-277-179907/milenial-generasi-
burnout - but i’m rejuvenated: A guide for individual kutu-loncat-pengubah-gaya-kerja
and organization. Bloomington: Author House. [57]. Rafiq, M., & Chin, T. (2019). Three-way interaction
[42]. Kinnunen, U., & Makikangas, A., Mauno, S., De effect of job insecurity, job embeddedness and career
Cuyper, N., & De Witte, H. (2014). Development of stage on life satisfaction in a digital era. International
perceived job insecurity across two years: Associations Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
with antecedents and employee outcomes. Journal of 16(9), 1-13. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16091580
Occupational Health Psychology. 19(2), 243–258. doi: [58]. Rajput, N., & Talan, A. (2017). Antecedents and health
10.1037/a0035835 consequences of job insecurity among teachers. Global
[43]. Kosztyán, Z. T., Csizmadiab, T., & Katona, A. I. Journal of Enterprise Information System, 9(2), 33-41.
(2021). SIMILAR – Systematic iterative multilayer doi: 10.18311/gjeis/2017/15704
literature review method. Journal of Informetrics, 15(1),
1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2020.101111
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 966
Volume 8, Issue 5, May – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
[59]. Richter, A., & Näswall, K. (2018). Job insecurity and [71]. Soomro, S. A., Kundi, Y. M., & Kamran, M. (2019).
trust: Uncovering a mechanism linking job insecurity to Antecedents of workplace deviance: Role of job
well-being. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group: Work insecurity, work stress, and ethical work climate.
& Stress, 33(1), 22-40. doi: Problemy Zarądzania – Management Issues, 17(6), 74-
10.1080/02678373.2018.1461709 90. doi: 10.7172/1644-9584.86.4
[60]. Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2018). Essentials of [72]. Spector, P. E., & O’Connell, B. J. (1994). The
Organizational behavior: Fourteenth edition. Harlow: contribution of personality traits, negative affectivity,
Pearson locus of control and type a to the subsequent reports of
[61]. Rothmann, I., & Cooper, C. (2008). Organizational and job stressors and job strains. Journal of Occupational
work psychology: Topics in applied psychology. and Organizational Psychology, 67(1), 1-12. doi:
London: Hodder Education 10.1111/j.2044-8325.1994.tb00545.x
[62]. Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2000). Intrinsic and [73]. Spector, P. E. (2022). Job satisfaction: From
extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new assessment to intervention. New York: Routledge.
directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, [74]. Stankeviˇciute, Ž., Staniškiene, E., & Ramanauskaite, J.
25(1), 54–67. doi: 10.1006/ceps.1999.1020 (2021). The impact of job insecurity on employee
[63]. Saeed, S., Hassan, I., Dastgeer, G., & Iqbal, T. (2021). happiness at work: A case of robotised production line
The route to well-being at workplace: Examining the operators in furniture industry in lithuania.
role of job insecurity and its antecedents. European Sustainability, 13(3), 1-20. doi: 10.3390/su13031563
Journal of Management and Business Economics, 1-26. [75]. Tangkilisan, H. N. S. (2007). Manajemen publik.
doi: 10.1108/EJMBE-02-2020-0025 Jakarta: PT Grasindo.
[64]. Schaufeli, W. B., Salanova, M., Gonzalez-Roma, V., & [76]. Tedja, T., & Sijabat, R. (2021). Analisis pengaruh
Bakker, A. B. (2002). The measurement of engagement perkembangan identitas terhadap intensi turnover
and burnout: A two sample confirmatory factor analytic dengan mediasi komitmen karier pada karyawan
approach. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3(1), 71–92. milenial jabodetabek. Widya Cipta: Jurnal Sekretari
doi: 10.1023/A:1015630930326 dan Manajemen, 5(2), 124-135. doi:
[65]. Schumacher, D., Schreurs, B., Van Emmerik, H., & De 10.31294/widyacipta.v5i2.10937
Witte, H. (2015). Explaining the relation between job [77]. VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2015). American
insecurity and employee outcomes during psychological association dictionary of psychology
organizational change: A multiple group comparison. second edition. London: American Psychological
Human Resources Management, 55(5), 809-827. doi: Assosiation
10.1002/hrm.21687 [78]. Vanhercke, D., De Cuyper, N., & Peeters, E. (2014).
[66]. Scott-Jackson, W., & Mayo, A. (2018). Transforming Defining perceived employability: A psychological
engagement, happiness, and well-being: Enthusing approach. Personnel Review, 43(4), 592-605. doi:
people, teams and nations. Berlin: Springer Nature. 10.1108/PR-07-2012-0110
[67]. Selenko, E., Makikangas, A., Mauno, S., & Kinnunen, [79]. Vujičić, D., Jovičić, A., Lalić, D., Gagić, S., &
U. (2013). How does job insecurity relate to self- Cvejanov, A. (2015). The relation between job
reported job performance? Analysing curvilinear insecurity, job satisfaction and organizational
associations in a longitudinal sample. Journal of commitment among employees in the tourism sector in
Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 86(4), novi sad. Economic and Industrial Democracy, 36(4),
522–542. doi: 10.1111/joop.12020 633-652. doi: 10.1177/0143831X14527017
[68]. Shin, Y., Hur, W. M., Moon, T. W., & Lee, S. (2019). A [80]. Wyland, R. L., Lester, S. W., Mone, M. A., & Winkel,
motivational perspective on job insecurity: D. E. (2013). Work and school at the same time? A
Relationships between job insecurity, intrinsic conflict perspective of the work-school conflict. Journal
motivation, and performance and behavioral outcomes. of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 20(3), 346-
International Journal of Environmental Research and 357. doi: 10.1177/1548051813484360
Public Health, 16(10), 1-16. doi: [81]. Wicaksono, P. A. (2007). Korelasi antara employees
10.3390/ijerph16101812 involvement, turnover serta pengaruhnya terhadap
[69]. Shoss, M. K. (2017). Job insecurity: An integrative produktivitas. Jurnal Teknik Industri, 2(1), 65-71. doi:
review and agenda for future research. Journal of 10.12777/jati.2.1.65-71
Management, 43(6), 1911-1939. doi: [82]. Wilkins, C. H. (2018). Effective engagement requires
10.1177/0149206317691574 trust and being trustworthy. Medical Care, 56(10), 6-8.
[70]. Soelton, M, Amaelia, P., & Prasetyo, H. (2019). doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000000953
Dealing with job insecurity, work stress, and family [83]. Wilkinson, K. (2022). Wellbeing at work. In S. Taylor
conflict of employees. Proceedings of the 4th & C. Woodhams (Eds.), Human resource management:
International Conference on Management, Economics people and organization (pp. 225-251). Kogan Page.
and Business, 120, 167-174. doi: [84]. World Health Organization. (2020). Occupational
10.2991/aebmr.k.200205.031 health: Stress at the workplace.
https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-
answers/item/ccupational-health-stress-at-the-workplace
IJISRT23MAY810 www.ijisrt.com 967
You might also like
- Employee Engagement in Contemporary Organizations: Maintaining High Productivity and Sustained CompetitivenessFrom EverandEmployee Engagement in Contemporary Organizations: Maintaining High Productivity and Sustained CompetitivenessNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument11 pages1 PBFildza ListyaningrumNo ratings yet
- 9 ArticleDocument10 pages9 Articlesiagh.sarahNo ratings yet
- Moderating Effect of Job Satisfaction On Turnover Intention and Stress Burnout Among Employees in The Information Technology SectorDocument7 pagesModerating Effect of Job Satisfaction On Turnover Intention and Stress Burnout Among Employees in The Information Technology SectorIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Impact of Organizational Culture and Work Environment On Occupational Health and Safety, Mediated by Work Motivation (At PT Manunggal Jaya Makmur)Document6 pagesImpact of Organizational Culture and Work Environment On Occupational Health and Safety, Mediated by Work Motivation (At PT Manunggal Jaya Makmur)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Proposal DefenseDocument16 pagesProposal Defensenilish22310119No ratings yet
- 386-Article Text-1343-1-10-20221102Document12 pages386-Article Text-1343-1-10-20221102Anne Clarisse DionisioNo ratings yet
- Stress Management and Employee Productivity An Examination of The Nigerian Work EnvironmentDocument8 pagesStress Management and Employee Productivity An Examination of The Nigerian Work EnvironmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document24 pagesPaper 1Madihah MazhanNo ratings yet
- Quality of Work Life, Job SatisfactionDocument9 pagesQuality of Work Life, Job SatisfactionVenkates PsnaNo ratings yet
- Workplace Well-Being and Work Engagement Among Employees in The Department of Public Works and Highways First and Third District Engineering OfficesDocument21 pagesWorkplace Well-Being and Work Engagement Among Employees in The Department of Public Works and Highways First and Third District Engineering OfficesIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- 201-Research Article-1491-1-10-20210706Document6 pages201-Research Article-1491-1-10-20210706anjaneyaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Employee Absenteeism at TVS Sundaram Fasteners Limited, Chennai, TamilnaduDocument7 pagesA Study On Employee Absenteeism at TVS Sundaram Fasteners Limited, Chennai, TamilnaduIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The 9 International Management Conference Management and Innovation For Competitive AdvantageDocument12 pagesProceedings of The 9 International Management Conference Management and Innovation For Competitive AdvantageDr-Rajshree Sharma PathakNo ratings yet
- Non Monetary Incentives NMI As A MotivatDocument8 pagesNon Monetary Incentives NMI As A MotivatSusan KiuNo ratings yet
- Job Stress and Productivity A Conceptual PDFDocument7 pagesJob Stress and Productivity A Conceptual PDFShazwan ShauqiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change Communication, Workplace Bullying and Job Insecurity: The Moderating Role of Trust in ManagementDocument14 pagesOrganizational Change Communication, Workplace Bullying and Job Insecurity: The Moderating Role of Trust in Management20220510507No ratings yet
- Employees Is A Key Player in The Training andDocument59 pagesEmployees Is A Key Player in The Training andHanafi Ibrahim Basara CapalNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument6 pagesResearch MethodologyMekhna VilsonNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Theoretical and Applied SciencesDocument9 pagesEuropean Journal of Theoretical and Applied SciencesEJTAS journalNo ratings yet
- Impact of Job Demands Attributes On Employees' Burnout With Reference To Manufacturing Companies in South IndiaDocument15 pagesImpact of Job Demands Attributes On Employees' Burnout With Reference To Manufacturing Companies in South Indiaindex PubNo ratings yet
- PUBLIKASIDocument16 pagesPUBLIKASIKharis MaulanaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionaskmeeNo ratings yet
- 00.the Impact of Need Satisfaction On Job Performance and Work EngagementDocument14 pages00.the Impact of Need Satisfaction On Job Performance and Work EngagementFAO oseiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Job Security, Features, Personal Values and Recognition On Organizational InvolvementDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Job Security, Features, Personal Values and Recognition On Organizational InvolvementJack petersNo ratings yet
- The Factors Which Affecting Turnover Intention Through Employee Engagement As A Mediation Variable (Case Study On XYZ Private Bank in Indonesia)Document9 pagesThe Factors Which Affecting Turnover Intention Through Employee Engagement As A Mediation Variable (Case Study On XYZ Private Bank in Indonesia)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Employee WellbeingDocument19 pagesEmployee Wellbeingrishika1504No ratings yet
- JMKI - VOLUME 1, NO. 3, JULI 2023 Hal 48-62Document15 pagesJMKI - VOLUME 1, NO. 3, JULI 2023 Hal 48-62Vanesa Amalia DuatiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Work-Life Balance Towards Employee Engagement in Millennial GenerationDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Work-Life Balance Towards Employee Engagement in Millennial GenerationKKN-T REGULER PERIODE II KELOMPOK 109 SEI KAYU 1No ratings yet
- Employee Engament PractisesDocument6 pagesEmployee Engament PractisesAbinash PandaNo ratings yet
- Skelton Et Al. - Predicting Manufacturing Employee Turnover IntentiDocument18 pagesSkelton Et Al. - Predicting Manufacturing Employee Turnover IntentiVictor Adrian Alvarez CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Ijems V343Document9 pagesIjems V343AnneNo ratings yet
- Effect of Employee Engagement On Perceived Corporate Social Responsibility in IT SectorDocument9 pagesEffect of Employee Engagement On Perceived Corporate Social Responsibility in IT SectorInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Job Satisfaction On Employee Turnover Intention in The Manufacturing Industry of MalaysiaDocument11 pagesThe Influence of Job Satisfaction On Employee Turnover Intention in The Manufacturing Industry of MalaysiaTrúc TrươngNo ratings yet
- Arathy & Biju (2021)Document23 pagesArathy & Biju (2021)JasleenNo ratings yet
- Participation in Decision-Making and Work Outcomes: Evidence From A Developing EconomyDocument20 pagesParticipation in Decision-Making and Work Outcomes: Evidence From A Developing EconomyMridula RajakNo ratings yet
- 1.my ProjectDocument60 pages1.my Projectzainabshittu45No ratings yet
- 439-Article Text-1022-1061-10-20230627Document9 pages439-Article Text-1022-1061-10-20230627HusnaanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CIPD Level 5 Formative AssignmentDocument10 pagesUnit 2 CIPD Level 5 Formative AssignmentJoanna Fortuna-QueirozNo ratings yet
- Well Being 04Document19 pagesWell Being 04Nischal RaoNo ratings yet
- Quality of Work Life and Employee Performance in Insurance SectorDocument24 pagesQuality of Work Life and Employee Performance in Insurance SectorAtreya PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction in Insurance Sector: An Empirical InvestigationDocument9 pagesJob Satisfaction in Insurance Sector: An Empirical Investigationcc ranchiNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction in Insurance Sector: An Empirical InvestigationDocument9 pagesJob Satisfaction in Insurance Sector: An Empirical InvestigationKeshika TNo ratings yet
- SummariesDocument7 pagesSummariesLakshay SukhijaNo ratings yet
- TAMBAOAN - Termination of Employee Relationship - 06.04.22v2.5Document10 pagesTAMBAOAN - Termination of Employee Relationship - 06.04.22v2.5NOLI TAMBAOANNo ratings yet
- Effects of Employee Engagement Toperfomance (Case Study: Insurance Company in Indonesia) Yona Melia, Nidya DudijaDocument10 pagesEffects of Employee Engagement Toperfomance (Case Study: Insurance Company in Indonesia) Yona Melia, Nidya DudijaSlamat RiadiNo ratings yet
- Coetzer Et Al Servant Leadership Well-BeingDocument11 pagesCoetzer Et Al Servant Leadership Well-BeingmelanyNo ratings yet
- Workplace Stress Implication For Organizational Performance in A Nigerian Public UniversityDocument10 pagesWorkplace Stress Implication For Organizational Performance in A Nigerian Public UniversitykinantimutzNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Employee Attrition Among IT Employees: R. ShanmugamDocument5 pagesAssessment of Employee Attrition Among IT Employees: R. ShanmugamRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat: Knowledge and Motivation With Safe Behavior of Informal Sector Female WorkerDocument13 pagesJurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat: Knowledge and Motivation With Safe Behavior of Informal Sector Female WorkerMyanmar LearnersNo ratings yet
- Internal Marketing, Employee Job Satisfaction, and Perceived Organizational Performance in Microfinance InstitutionsDocument24 pagesInternal Marketing, Employee Job Satisfaction, and Perceived Organizational Performance in Microfinance InstitutionsHenryawan SigitNo ratings yet
- Impact of Workplace Bullying On Job Performance, Intention To Leave, OCB and StressDocument29 pagesImpact of Workplace Bullying On Job Performance, Intention To Leave, OCB and Stresstony pauloNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Job Stress and Employee Performance in Manufacturing Industry in IndonesiaDocument13 pagesThe Relationship Between Job Stress and Employee Performance in Manufacturing Industry in IndonesiaQuyen MyNo ratings yet
- Paper 9 - IJMET - 10 - 02 - 044 - QUALITY OF WORK-LIFE ANDDocument13 pagesPaper 9 - IJMET - 10 - 02 - 044 - QUALITY OF WORK-LIFE ANDHussein OlowuNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument37 pagesDissertationvee audyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0970389618302374 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0970389618302374 Maindata rabiqyNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Interrelationships Between Employee Engagement, Employee Engagement Initiatives and Job SatisfactionDocument27 pagesA Study On The Interrelationships Between Employee Engagement, Employee Engagement Initiatives and Job Satisfactionnivis7979No ratings yet
- A Literature Review On Employee RetentioDocument7 pagesA Literature Review On Employee RetentioSumerNo ratings yet
- Junaidi Et Al (WL & Ti)Document6 pagesJunaidi Et Al (WL & Ti)vindi putri kurnia illahiNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Employee Engagement: January 2018Document13 pagesLiterature Review On Employee Engagement: January 2018shriyaNo ratings yet
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocument6 pagesStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Document8 pagesAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocument8 pagesUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocument7 pagesBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocument33 pagesCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Forensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsDocument12 pagesForensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Health Care SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocument6 pagesImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDocument4 pagesCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDocument19 pagesSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocument2 pagesParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDocument2 pagesPredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalDocument7 pagesKeywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDocument8 pagesInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDocument6 pagesImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDocument5 pagesParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolDocument31 pagesThe Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDocument8 pagesAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Quantifying of Radioactive Elements in Soil, Water and Plant Samples Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) TechniqueDocument6 pagesQuantifying of Radioactive Elements in Soil, Water and Plant Samples Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Investigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatDocument16 pagesInvestigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsDocument6 pagesAn Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Harnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesDocument7 pagesHarnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 pagesAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIDocument6 pagesThe Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterDocument11 pagesThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Terracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonDocument14 pagesTerracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Psychological Explanations of CrimeDocument45 pagesPsychological Explanations of CrimeGerald WopataNo ratings yet
- Assignment PersuasionDocument6 pagesAssignment PersuasionKartiki SinghNo ratings yet
- 3as Accomplishmenr Report Q2Document9 pages3as Accomplishmenr Report Q2Melanie Ibarra CarlosNo ratings yet
- CHAP-1-Organizational BehaviorDocument34 pagesCHAP-1-Organizational BehaviorYen HoangNo ratings yet
- MPOBDocument37 pagesMPOBGarvit JainNo ratings yet
- DLL Kinder w7Document6 pagesDLL Kinder w7Mel Rose Cabrera100% (1)
- All About NPD (Narcissistic Personality Disorder) : Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesAll About NPD (Narcissistic Personality Disorder) : Abnormal PsychologyKyle Sanchez (Kylie)No ratings yet
- PLP GabrielDocument5 pagesPLP Gabrielapi-392613490No ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature (RRL)Document8 pagesReview of Related Literature (RRL)Shaira Mae Mordido GudiagaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Consequences of Sexual AbuseDocument5 pagesCauses and Consequences of Sexual AbuseRosa HuaracheNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs ExplainedDocument12 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs ExplainedwojacaNo ratings yet
- BelbinTeam QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesBelbinTeam QuestionnaireTPMOffice BajajNo ratings yet
- The Field of Social PsychologyDocument11 pagesThe Field of Social PsychologyRaja Bilal JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Team DevelopmentDocument2 pagesStages of Team DevelopmentBrittanyNo ratings yet
- Fear of Missing Out (FoMO) in Analysis of Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)Document4 pagesFear of Missing Out (FoMO) in Analysis of Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)Gibran LeandroNo ratings yet
- TRF Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesTRF Questions and Answersjernalynluzano100% (1)
- Reference Letter - Jessica LevanDocument2 pagesReference Letter - Jessica Levanapi-531737462No ratings yet
- A Model For Arts-Based Interventions in The School SettingDocument65 pagesA Model For Arts-Based Interventions in The School SettingRodelyn Stoeber100% (1)
- Canadian WorkplaceDocument5 pagesCanadian WorkplaceGuo NicNo ratings yet
- SHS Humss Ucsp Q1 WK3Document4 pagesSHS Humss Ucsp Q1 WK3Axel Crusit MesagrandeNo ratings yet
- Media Children Indpendent Study-4-2Document21 pagesMedia Children Indpendent Study-4-2api-610458976No ratings yet
- 157 239 1 PBDocument10 pages157 239 1 PBJhade ManatigaNo ratings yet
- Homeroom ActivityDocument8 pagesHomeroom ActivityClarence HubillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Meaning and Relevance of Educational PsychologyDocument12 pagesTopic 1 Meaning and Relevance of Educational PsychologyKibetfredrickNo ratings yet
- Ucsp 2ND SlidesDocument21 pagesUcsp 2ND SlidesBangi, Jamby M.100% (1)
- Team WorkDocument23 pagesTeam WorkNkhasi NqosaNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion in CookeryDocument2 pagesWork Immersion in CookeryJamaica Trixia E BNo ratings yet
- 47 Terms That Describe Sexual AttractionDocument8 pages47 Terms That Describe Sexual AttractionPKBI SULAWESI UTARANo ratings yet
- EDUC-5410 Written Assignment 2Document5 pagesEDUC-5410 Written Assignment 2angeli abuegNo ratings yet
- Ken Don 1986Document14 pagesKen Don 1986Ivaylo DagnevNo ratings yet
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinFrom EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessFrom EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- Your Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesFrom EverandYour Creative Mind: How to Disrupt Your Thinking, Abandon Your Comfort Zone, and Develop Bold New StrategiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Summary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyFrom EverandSummary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Small Business For Dummies: 5th EditionFrom EverandSmall Business For Dummies: 5th EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyFrom EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingFrom EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesFrom Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeFrom EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Play Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsFrom EverandPlay Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- How to Think Strategically: Upskilling for Impact and Powerful StrategyFrom EverandHow to Think Strategically: Upskilling for Impact and Powerful StrategyNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing RiskFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing RiskRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Jim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryFrom EverandJim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Learn and Understand Business AnalysisFrom EverandLearn and Understand Business AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (31)
- The Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeFrom EverandThe Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)